The Evolution of Chatbots: From Rule-Based Scripts to AI-Powered NLP Assistants
Chatbots are no longer clunky scripts. Thanks to NLP, they’ve become intelligent assistants capable of understanding context, sentiment, and intent. Here’s how conversational AI evolved—and what it means for businesses.
TrendFlash
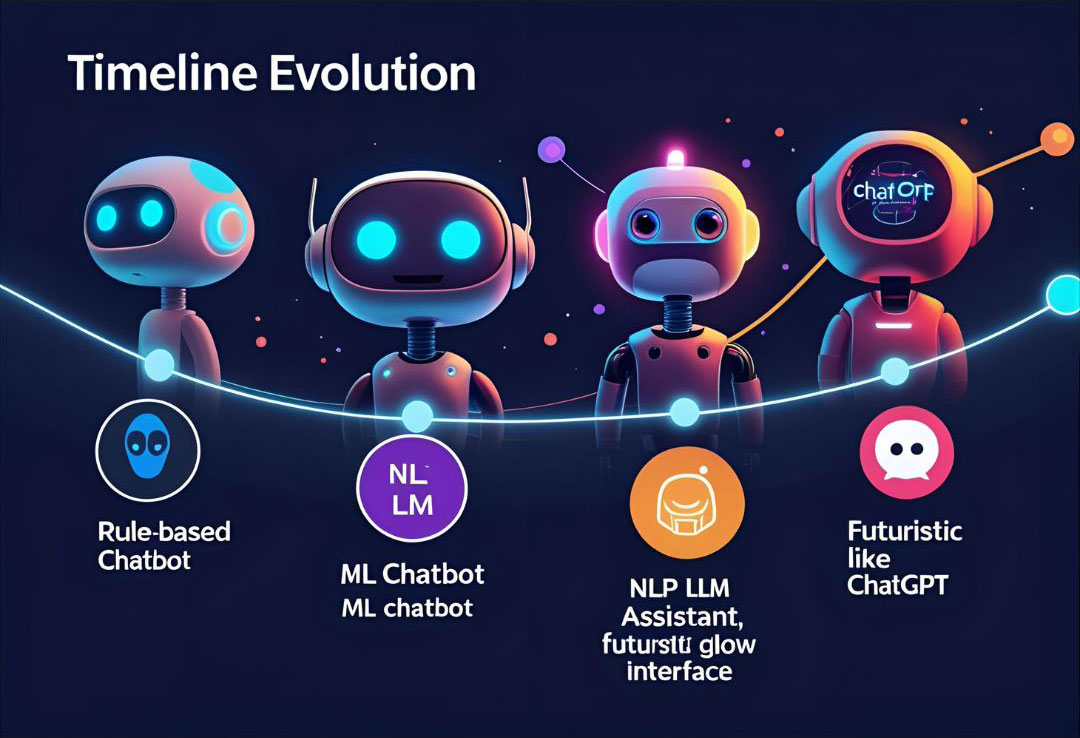
Introduction: From Eliza to ChatGPT
Chatbots have come a remarkably long way. In the 1960s, ELIZA fooled people into thinking they were conversing with a therapist by reflecting statements back at them. In 2025, chatbots like ChatGPT engage in sophisticated multi-turn conversations, answer complex questions, write code, and reason about abstract concepts.
This evolution reflects the dramatic progress in natural language processing and machine learning. Understanding this evolution provides insight into how AI progresses and why modern chatbots are so much more capable than their predecessors.
Phase 1: Rule-Based Chatbots (1960s-1990s)
The ELIZA Experiment
ELIZA, created by Joseph Weizenbaum in 1964, demonstrated that humans anthropomorphize machines. By mimicking a Rogerian psychotherapist through pattern matching and substitution, ELIZA convinced people they were speaking with a human therapist.
Limitations: No actual understanding. Rigidly pattern-matched responses. Failed with any deviation from expected input patterns.
Template-Based Systems
Subsequent rule-based chatbots used hand-coded templates mapping inputs to outputs.
Example:
- Input: "What is the weather?"
- Pattern: "What is [X]?"
- Response: "I don't have access to current weather information."
Applications: Customer service FAQs, basic information retrieval.
Phase 2: Machine Learning Chatbots (1990s-2010s)
Intent Recognition
Rather than pattern matching, ML-based chatbots classified user input into intents (e.g., "order_pizza", "check_status", "get_help").
Process:
- Extract features from user input
- Classify into intent category using trained classifier
- Retrieve appropriate response
Vast improvement: Handles variations in user phrasing, learns from data rather than requiring explicit rules.
Statistical Language Models
Rather than retrieving pre-written responses, systems could generate responses using learned patterns. Techniques like N-gram models and Hidden Markov Models enabled this.
Real-World Impact
By 2010, ML-based chatbots handled significant customer service volume across industries, improving response consistency and availability.
Phase 3: Neural Network & Deep Learning Era (2010s)
Sequence-to-Sequence Models
RNNs and LSTMs enabled end-to-end learning of conversation patterns. Encoder-decoder architectures could learn to map user statements to appropriate responses directly.
Embedding Spaces
Word embeddings (Word2Vec) captured semantic relationships between words. Chatbots could understand that "happy" and "pleased" are similar, enabling better generalization.
Context and Memory
Neural networks could maintain context across multi-turn conversations, enabling coherent extended dialogues rather than isolated question-answer pairs.
Phase 4: Transformer & Large Language Models (2018-2025)
The ChatGPT Revolution
Large pre-trained language models like GPT-3, GPT-4, Claude, and Gemini fundamentally changed chatbot capabilities. Rather than training task-specific models on limited data, these systems:
- Train on trillions of tokens of diverse text
- Capture general language knowledge and reasoning patterns
- Fine-tune on relatively modest amounts of dialogue data
- Produce remarkably coherent, contextually appropriate responses
Capabilities Leap
Modern chatbots now:
- Understand nuanced questions with multiple interpretations
- Maintain consistent personas across conversations
- Generate creative content (stories, poems, code)
- Reason about complex scenarios
- Admit uncertainty appropriately
- Engage in Socratic dialogue
Real-Time Voice Interactions
Real-time voice agents now conduct natural conversations with human latency characteristics, enabling voice-based customer service, accessibility tools, and interactive applications.
From Chatbots to Agents: The Next Evolution
Limitations of Conversational Chatbots
- Passive: wait for user input
- Stateless: can't take action in external systems
- Hallucinatory: can confidently provide false information
- Limited knowledge: constrained by training data cutoff
The Agent Transition
Agentic AI extends beyond conversation to action. Agents:
- Plan multi-step sequences toward goals
- Call external tools and APIs
- Maintain state and memory
- Learn from feedback
- Operate autonomously
This represents a fundamental shift from "chat with AI" to "AI does things for you."
Practical Deployment: Building Chatbots Today
Platforms and Tools
- OpenAI API: Access to GPT-4 and latest models
- Google Vertex AI: Gemini models with enterprise features
- Anthropic Claude: Strong reasoning and safety focus
- Open Source: Llama, Mixtral, other community models
Architecture Considerations
- Real-time latency requirements drive model size decisions
- Accuracy vs. cost trade-offs
- Knowledge base integration (RAG) for factual grounding
- Safety filters for appropriate outputs
Conclusion: The Chatbot-to-Agent Transition
Chatbots have evolved from rigid rule-based systems to sophisticated language models capable of reasoning and generating creative content. The next evolution—autonomous agents—represents another quantum leap.
Explore: AI customer service agents, voice agents, all AI trends.
Share this post
Categories
Recent Posts
Opening the Black Box: AI's New Mandate in Science
AI as Lead Scientist: The Hunt for Breakthroughs in 2026
Measuring the AI Economy: Dashboards Replace Guesswork in 2026
Your New Teammate: How Agentic AI is Redefining Every Job in 2026
Related Posts
Continue reading more about AI and machine learning

Prompt Engineering 2.0: How to Write Prompts That Understand You (Not the Other Way Around)
The era of simple keyword prompts is over. Discover how Prompt Engineering 2.0 uses structured commands, specific personas, and strategic framing to make advanced AI models like GPT-4 and Claude 3 deliver precisely what you need.

AI Hallucinations Are Getting More Dangerous: How to Spot and Stop Them in 2025
AI isn't just making up facts anymore; it's creating convincing, dangerous fabrications. Discover why modern hallucinations are harder to detect and how new mitigation techniques are essential for any business using AI in 2025.
Natural Language Processing: How AI Understands Human Language in 2025
NLP technology has advanced to near-human understanding of language. This guide explains how AI processes text and speech with unprecedented accuracy in 2025.