10 Machine Learning Algorithms Every Developer Should Master (2025 Guide)
Machine learning powers today’s most impactful AI systems. But which algorithms actually matter in practice? This guide walks through 10 essential ML algorithms every developer should understand, along with use-cases, pitfalls, and evaluation tips.
TrendFlash
Introduction: Why Algorithm Knowledge Still Matters in 2025
In an era of pre-trained models and AutoML platforms, do developers still need to understand individual machine learning algorithms? The answer is unequivocally yes. While high-level frameworks abstract away implementation details, understanding how algorithms work enables you to debug failures, optimize performance, choose appropriate techniques for specific problems, and innovate beyond what existing tools provide.
This comprehensive guide covers 10 essential algorithms that remain foundational in 2025, even as the AI landscape evolves toward larger models and more automated approaches. Whether you're building machine learning systems, developing AI productivity tools, or pursuing an AI career, this knowledge forms an essential foundation.
1. Linear Regression: The Foundation of Predictive Analytics
Core Concept
Linear regression is the simplest supervised learning algorithm, modeling the relationship between input features and a continuous output variable using a straight line (or hyperplane in multiple dimensions).
Mathematical Foundation
The algorithm finds optimal coefficients (weights) by minimizing the difference between predicted and actual values. Despite its simplicity, linear regression teaches fundamental ML concepts: loss functions, gradient descent optimization, and regularization techniques.
Best Use Cases
- Housing price prediction from features like square footage and location
- Sales forecasting based on historical trends
- Demand estimation for inventory planning
- Risk scoring in financial applications
Strengths & Limitations
Strengths: Interpretable, computationally efficient, fast to train, works well when relationships are approximately linear.
Limitations: Assumes linear relationships; highly sensitive to outliers; poor performance when data violates linearity assumptions.
Evaluation Metrics
- RMSE (Root Mean Squared Error): Penalizes large errors heavily
- MAE (Mean Absolute Error): Average magnitude of errors
- R² Score: Proportion of variance explained (0-1 scale)
- Residual Plots: Visual inspection of error patterns
In practice, always examine residual plots to ensure linear regression's assumptions hold before deploying models in production.
Conclusion: Mastering Foundational Algorithms
Master these algorithms, and you'll understand the reasoning behind virtually any machine learning system. You'll know when to apply which technique, how to debug failures, and how to innovate beyond existing approaches.
The future belongs to those who understand these fundamentals deeply enough to build on them creatively. Start here, go deeper, and contribute to the next evolution of intelligent systems.
Continue your learning journey with our comprehensive guides on the latest ML algorithms, recent breakthroughs, and emerging AI trends.
Tags
Share this post
Categories
Recent Posts
Opening the Black Box: AI's New Mandate in Science
AI as Lead Scientist: The Hunt for Breakthroughs in 2026
Measuring the AI Economy: Dashboards Replace Guesswork in 2026
Your New Teammate: How Agentic AI is Redefining Every Job in 2026
Related Posts
Continue reading more about AI and machine learning
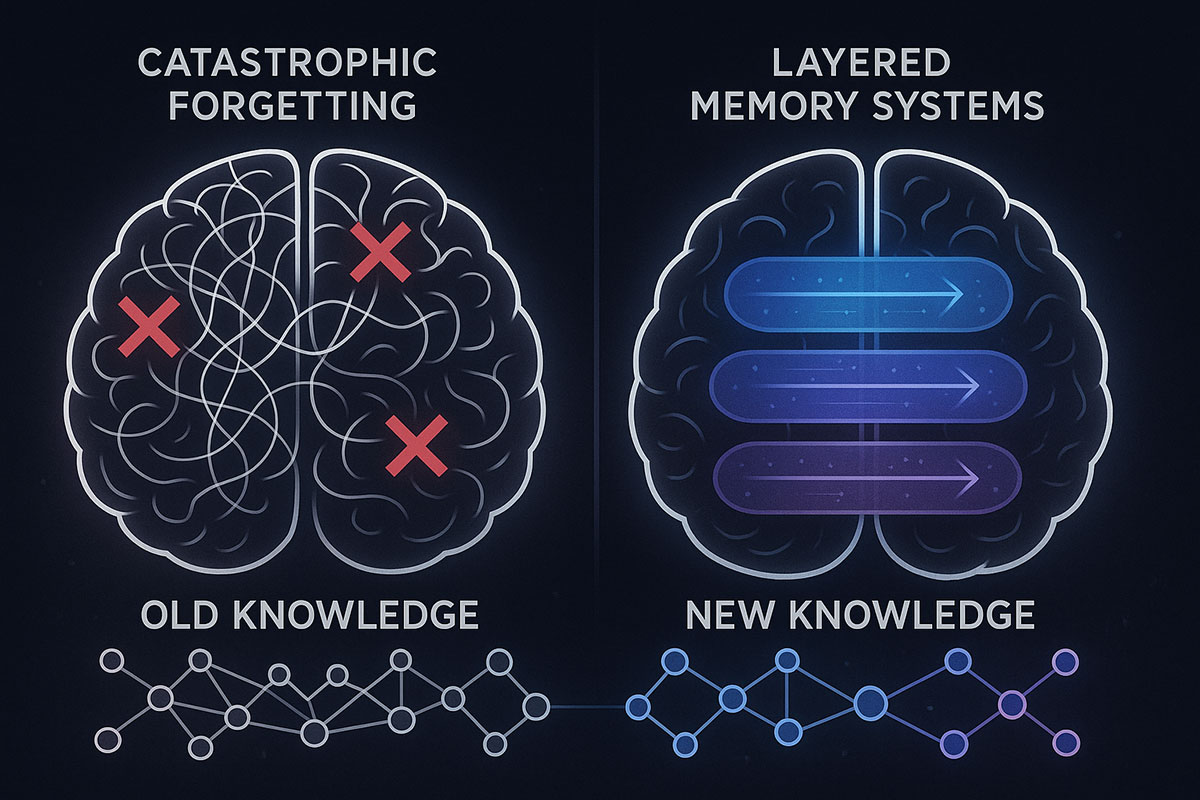
Google's HOPE Model: AI That Finally Learns Continuously (Catastrophic Forgetting Solved)
Google just unveiled HOPE, a self-modifying AI architecture that solves catastrophic forgetting—the fundamental problem preventing AI from learning continuously. For the first time, AI can absorb new knowledge without erasing what it already knows. Here's why this changes everything.
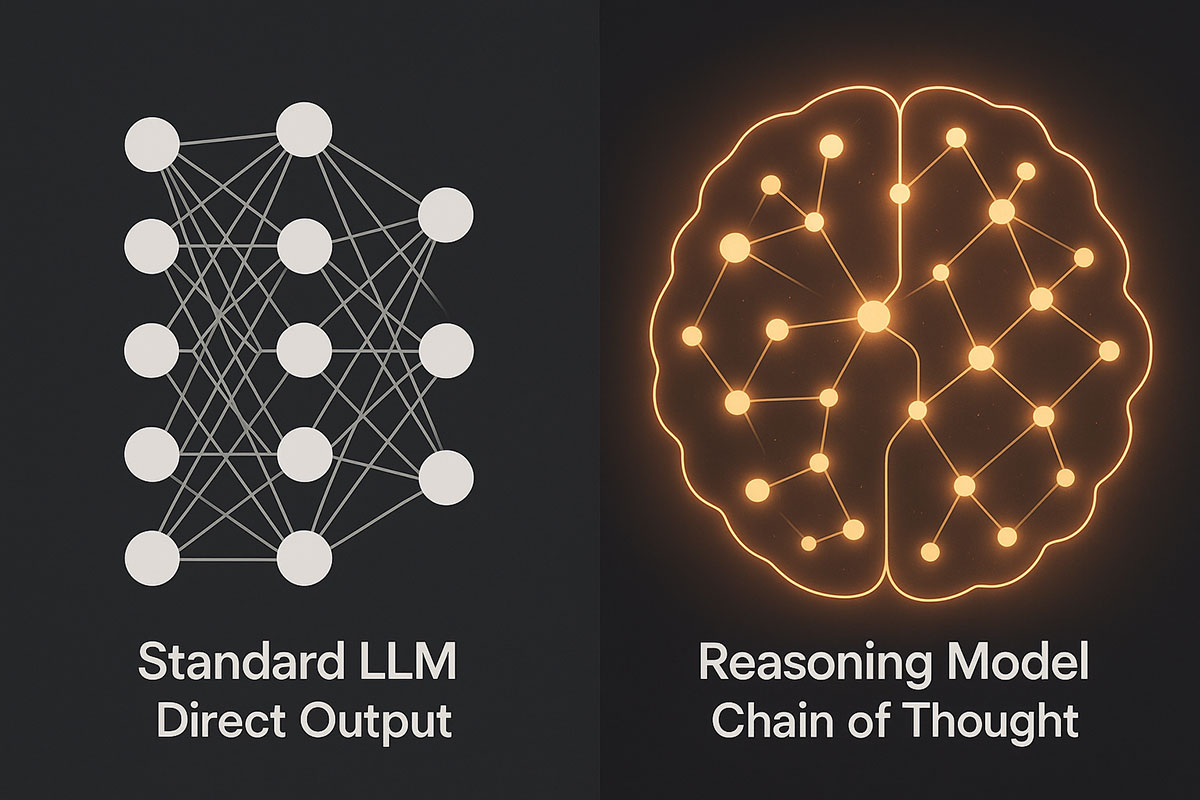
AI Reasoning Models Explained: OpenAI O1 vs DeepSeek V3.2 - The Next Leap Beyond Standard LLMs (November 2025)
Reasoning models represent a fundamental shift in AI architecture. Unlike standard language models that generate answers instantly, these systems deliberately "think" through problems step-by-step, achieving breakthrough performance in mathematics, coding, and scientific reasoning. Discover how O1 and DeepSeek V3.2 are redefining what AI can accomplish.
Why Smaller AI Models (SLMs) Will Dominate Over Large Language Models in 2025: The On-Device AI Revolution
The AI landscape is shifting from "bigger is better" to "right-sized is smarter." Small Language Models (SLMs) are delivering superior business outcomes compared to massive LLMs through dramatic cost reductions, faster inference, on-device privacy, and domain-specific accuracy. This 2025 guide explores why SLMs represent the future of enterprise AI.