Reinforcement Learning in 2025: From Games to Real-World Automation
Reinforcement learning is no longer just for games. In 2025, it powers robotics, logistics, healthcare, and autonomous decision-making.
TrendFlash

Introduction: The Regulatory Race
As AI becomes more powerful, governments are scrambling to regulate it. But they're not coordinating. The result: a fragmented global landscape where the same AI system is legal in one place, illegal in another. This creates winners, losers, and confusion for everyone involved.
This guide explains how different regions are regulating AI and what it means for the future.
The EU Approach: The AI Act
What Is It?
The most comprehensive AI regulation globally
Status: Went into effect January 2024 (enforcement ongoing)
Key Provisions
Risk-Based Classification:
- Prohibited AI: Social credit scores, real-time biometric surveillance (banned)
- High-Risk AI: Hiring, criminal justice, lending (heavy regulation)
- Medium-Risk: Transparency requirements
- Low-Risk: Minimal regulation
Transparency Requirements: AI systems must disclose they're AI
Right to Explanation: Users can ask why AI made decisions about them
Bias Testing: High-risk systems must be tested for discrimination
Fines: Up to €30M or 6% of global revenue (whichever is higher)
Impact
For Companies: Increased compliance costs, regulatory burden
For Consumers: More protection, right to explanation, reduced bias
For Innovation: EU becoming less attractive for AI startups (some moving to US)
Global Influence: Companies operating globally follow EU rules (highest bar sets global standard)
The US Approach: Fragmented & Sector-Specific
What Is It?
No single AI law. Instead, sector-specific rules
Key Regulations
By Sector:
- Finance: Fair Lending rules, algorithmic transparency
- Healthcare: FDA approval for medical AI
- Employment: EEOC enforcing against algorithmic discrimination
- Consumer Protection: FTC regulating AI advertising and privacy
Executive Orders: Biden administration pushing AI safety research (not binding)
NIST AI Risk Management Framework: Guidance (not legally required)
Impact
For Companies: Unclear requirements, piecemeal compliance
For Innovation: More freedom than EU (faster development)
For Consumers: Less comprehensive protection than EU
Competitive Advantage: US AI companies move faster than EU counterparts
China's Approach: State Control
What Is It?
AI heavily integrated with state control mechanisms
Key Policies
Content Control: Algorithms must not promote "harmful content" (government defines this)
Data Localization: AI data must stay in China (no cloud transfers abroad)
State Oversight: Government approval needed for some AI applications
Social Credit Integration: AI feeds into social credit systems
Impact
For Innovation: Companies must serve government agenda
For Privacy: Minimal, used for population monitoring
For Geopolitics: China developing independent AI capabilities (not reliant on US)
Competitive Advantage: Can move faster (no democratic debate), but at cost of freedom
Other Regions
UK
Approach: Principles-based (rather than prescriptive)
Principle: Companies should be transparent and fair, but how is up to them
Advantage: Flexibility, faster innovation
Disadvantage: Less clear what's required
Canada
Approach: Bill C-27 (AI and data privacy)
Status: Still being debated
Likely: Similar to EU but less strict
Brazil
Approach: Bill 2338 (comprehensive AI law)
Status: Expected to pass 2025
Japan
Approach: Guidelines rather than law
Stance: Supportive of AI innovation with ethical guidelines
The Fragmentation Problem
The Reality
Same AI system faces:
- Legal in US (minimal regulation)
- Illegal in EU (fails AI Act requirements)
- Required by China (must report to government)
For Companies
Option 1: Build different versions for each region (expensive)
Option 2: Follow strictest rules everywhere (EU standard, reduces innovation)
Option 3: Exit some markets (lose revenue)
For Innovation
Negative: Companies discouraged from risky innovation
Positive: Reduces reckless AI deployment
For Geopolitics
US + EU + Others: Democratic AI governance
China: Authoritarian AI governance
Gap: Growing, creating tech decoupling
The Future of AI Regulation
2025-2026: Convergence Emerging
- More countries adopting EU-like frameworks
- US considering federal AI law
- International discussions on standards
2027-2030: Global Standards?
- ISO standards for AI development
- International frameworks (similar to financial regulation)
- Some convergence around core principles
Likely Core Principles
- Transparency (disclose AI use)
- Fairness (no illegal discrimination)
- Accountability (responsibility for harms)
- Privacy (data protection)
- Safety (robustness and security)
What This Means for You
If You're Building AI
- Assume EU rules as baseline
- Design for transparency and fairness
- Document decisions and testing
- Be prepared for different regional rules
If You're Using AI
- Understand your legal obligations
- Follow strictest rules applicable to you
- Stay informed as regulations evolve
If You're Considering AI Startup
- Choose market based on regulation
- EU stricter but larger market
- US faster but less regulated
- China fastest but most constrained
Conclusion: Regulation Is Here to Stay
AI regulation is not going away. The question is how fragmented it will be and how it will evolve. Understanding the current landscape and preparing for future changes is essential for anyone building or deploying AI.
Explore more on AI regulation and governance at TrendFlash.
Share this post
Categories
Recent Posts
Opening the Black Box: AI's New Mandate in Science
AI as Lead Scientist: The Hunt for Breakthroughs in 2026
Measuring the AI Economy: Dashboards Replace Guesswork in 2026
Your New Teammate: How Agentic AI is Redefining Every Job in 2026
Related Posts
Continue reading more about AI and machine learning
Opening the Black Box: AI's New Mandate in Science
AI is discovering proteins and simulating complex systems, but can we trust its answers if we don't understand its reasoning? The scientific community has issued a new mandate: open the black box. We explore the cutting-edge techniques transforming AI from an opaque predictor into a transparent, reasoning partner in the scientific process.
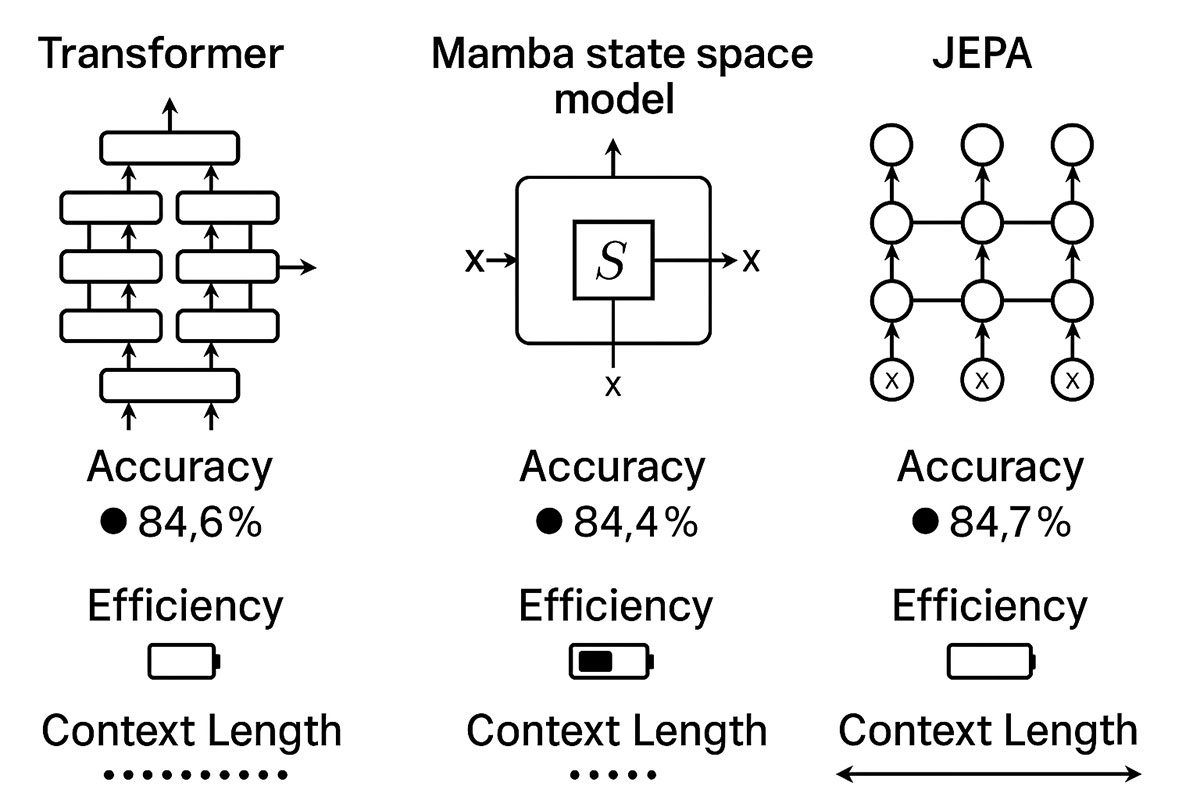
Deep Learning Architectures That Actually Work in 2025: From Transformers to Mamba to JEPA Explained
The deep learning landscape is shifting dramatically. While Transformers dominated the past five years, emerging architectures like Mamba and JEPA are challenging the status quo with superior efficiency, longer context windows, and competitive accuracy. This guide compares real-world performance, implementation complexity, and use cases to help you choose the right architecture.
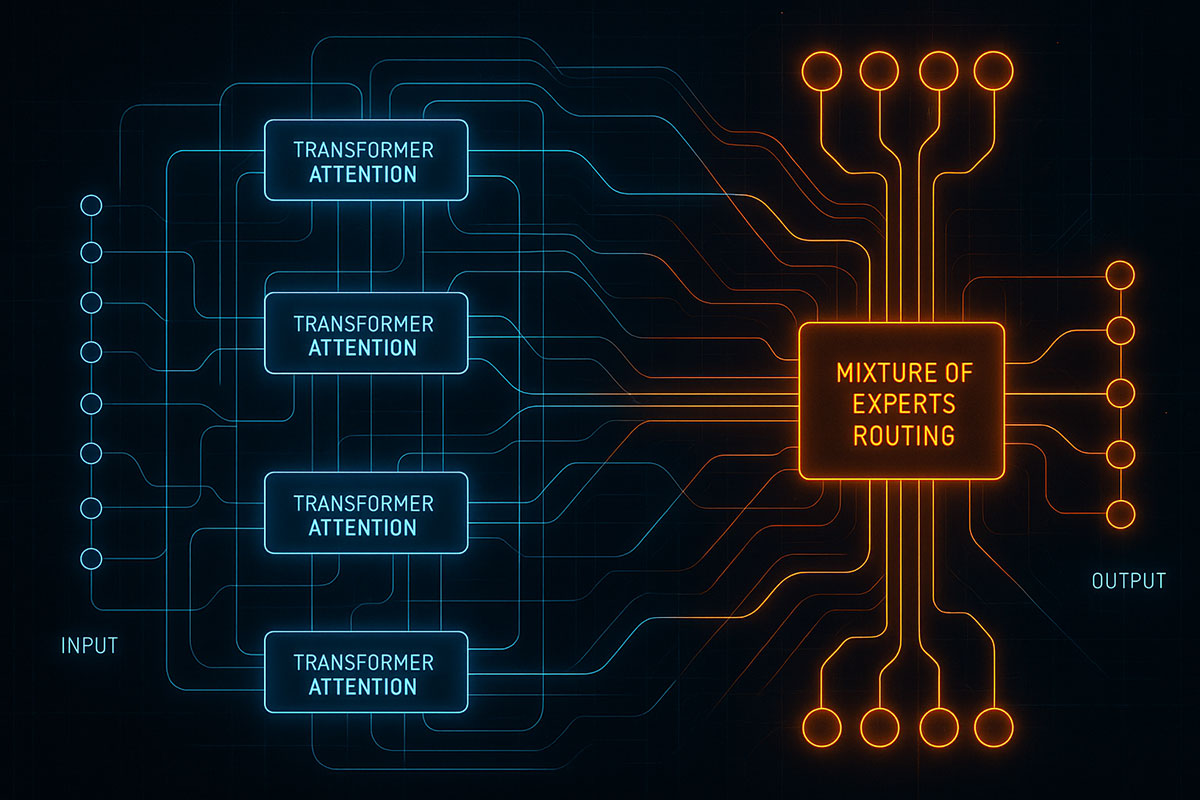
Deep Learning Architectures You Need to Know in 2025
From Transformers dominating NLP to Mixture of Experts revolutionizing efficiency, discover the deep learning architectures shaping AI innovation in 2025 and beyond.