OpenAI's New AI Browser (Atlas) Explained: How AI-Powered Web Browsing Changes Everything in 2025
OpenAI just launched Atlas, an AI-powered browser that fundamentally reimagines how we interact with the web. Built on Chromium but with ChatGPT at its core, Atlas lets you chat with websites, automate complex tasks, and browse smarter. Here's what you need to know about this paradigm shift.
TrendFlash
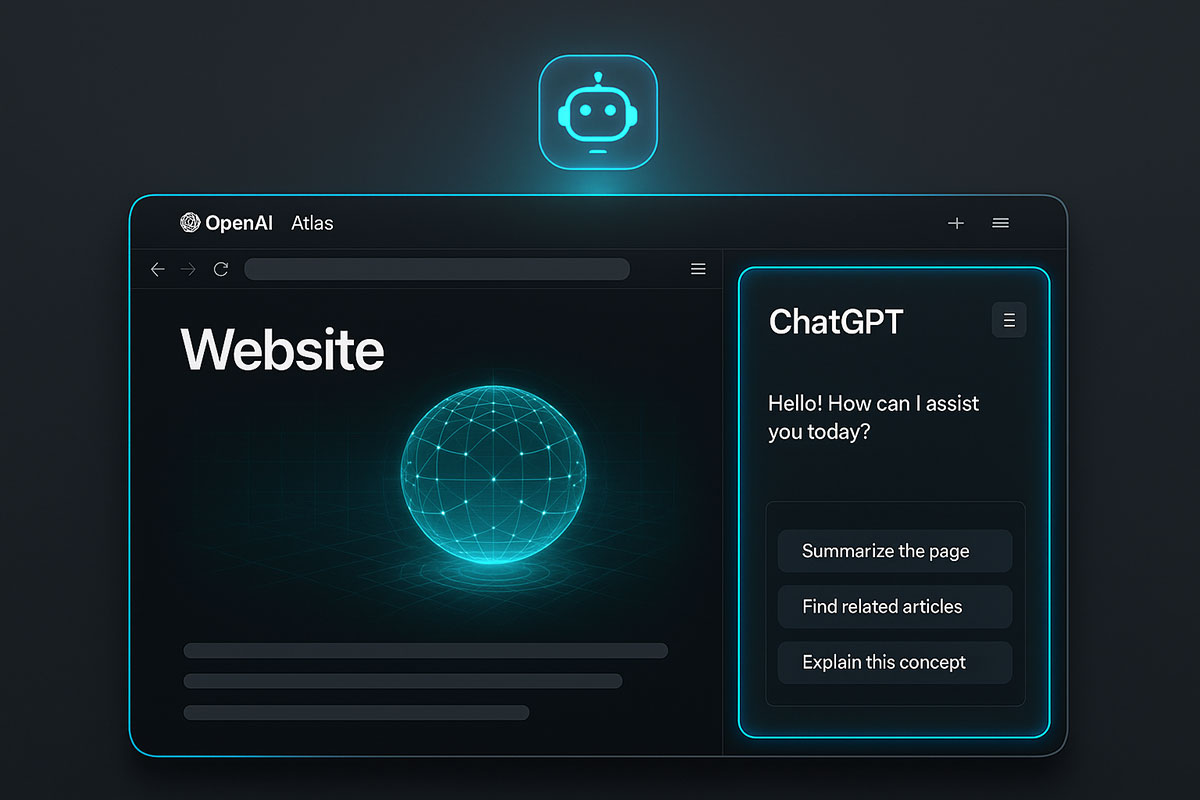
The Browser Wars Just Changed: Introducing OpenAI's Atlas
For decades, the browser has been the gateway to the internet. Google Chrome built an empire by being fast and simple. Then Microsoft Edge added AI features. Google launched AI Mode. But in October 2025, OpenAI made a move that fundamentally redefined what a browser can do. They didn't just add AI to a browser—they built a browser around AI.
Enter ChatGPT Atlas, an AI-native browser that treats ChatGPT not as an add-on, but as the core architecture. This isn't an incremental improvement. It's a paradigm shift. And it signals something bigger: the browser as we know it is evolving from a passive information retrieval tool into an active, intelligent co-worker that thinks, remembers, and acts on your behalf.
What Makes Atlas Different From Every Other Browser?
Traditional browsers—Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge—are fundamentally the same. They render pages, manage tabs, and handle bookmarks. The main differences are speed, privacy, and extensions. All are passive. You tell them where to go, and they take you there.
Atlas inverts this model. Instead of being a tool that retrieves information, Atlas becomes a partner that understands information, contextualizes it, and acts upon it.
Core Architecture: ChatGPT at the Center
Atlas is built on Chromium (the same foundation as Chrome and Edge), which means it's fast, standards-compliant, and capable of running billions of websites without friction. But instead of a traditional search bar, Atlas has something revolutionary: a persistent ChatGPT sidebar that lives alongside every webpage you visit.
This might sound like just another browser extension, but it's fundamentally different. The sidebar isn't an afterthought—it's the primary interface. You don't need to copy-paste content into ChatGPT. You don't need to switch tabs. ChatGPT sees what you see, in real-time, and can analyze, summarize, or act on it instantly.
The Three Pillars of Atlas: Chat, Memory, and Agency
Atlas rests on three revolutionary capabilities that redefine browser functionality.
Pillar 1: Chat Anywhere on the Web
Imagine you're reading a dense research paper, comparing product specs, or reviewing code on GitHub. Traditionally, you'd highlight text, copy it, open ChatGPT in a new tab, paste it, and ask your question. With Atlas, you simply open the sidebar and ask your question in context.
You can:
- Highlight a paragraph and ask, "What does this mean?" and get an instant explanation
- Compare prices across three shopping pages without leaving the tab
- Ask ChatGPT to refine the tone of an email you're composing directly in Gmail
- Request a summary of a long article and get key points in seconds
- Extract data from tables and have ChatGPT reorganize it
This eliminates what users have called "copy-paste hell." You maintain context, velocity, and flow. Your browser becomes a conversational interface to the entire internet.
Pillar 2: Browser Memories—The Intelligent Memory Bank
Atlas includes an optional feature called Browser Memories, which fundamentally changes how personalized browsing works. Unlike traditional browsing history, which is just a log of URLs, Browser Memories lets ChatGPT remember facts, insights, and patterns from your activity.
Here's what that means in practice:
- You can ask, "Find all the job postings I viewed last week and create an overview of industry trends," and Atlas will retrieve and synthesize that information
- If you're researching something across multiple sessions, Atlas remembers your context and can pick up where you left off
- If you prefer metric units, shortlist 14-inch laptops, or have specific product interests, Atlas learns these preferences and applies them to future searches and recommendations
- Atlas can suggest next steps—whether that's returning to past pages, diving deeper into topics, or surfacing related research
Critically, Browser Memories are opt-in and fully user-controlled. You can view all memories in settings, archive ones you don't need, and delete them by clearing your browsing history. You can also toggle memories off for specific sites, and use Incognito mode to ensure certain sessions aren't saved at all.
This feature represents a massive departure from traditional browsers. It transforms Atlas from a retrieval tool into a learning tool—one that gets smarter and more helpful the more you use it.
Pillar 3: Agent Mode—AI That Acts for You (Preview)
The most ambitious feature in Atlas is Agent Mode, currently available in preview to ChatGPT Plus and Pro subscribers. Agent Mode allows ChatGPT to take autonomous action within your browser on your behalf.
This goes far beyond automation scripts. With Agent Mode enabled, you can ask Atlas to:
- Book a flight by comparing options, checking your preferences, and completing the reservation
- Conduct competitive research by navigating to competitor websites, collecting claims, and drafting a side-by-side comparison
- Add grocery items to your cart, apply coupons, and proceed to checkout
- Search for specific products, narrow down options based on your criteria, and create a shortlist for your review
- Edit documents, fill out forms, and prepare reports across multiple tabs and websites
- Conduct market research by scanning news, pulling relevant quotes, and drafting a summary brief
The critical difference from pure automation: you maintain oversight. You can see what Atlas is doing, approve each step, and interrupt at any time. OpenAI has built strict safety boundaries into Agent Mode—it cannot access your local filesystem, download files, access saved passwords, or interact with financial sites without explicit user supervision on each action.
This is where the real productivity multiplication happens. What used to require an hour of manual research now takes minutes. What required switching between six applications becomes a single conversational interface.
How Atlas Compares to Traditional Browsers and Emerging Competitors
The browser landscape is fragmented, and understanding where Atlas fits requires comparing it to established players and new entrants.
| Feature | Atlas | Chrome | Edge | Firefox | Brave |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AI Integration | Native ChatGPT | Gemini extensions | Copilot sidebar | Limited | Limited |
| Task Automation | Agent Mode (preview) | Extensions only | Limited automation | Extensions only | No |
| Browser Memory | Yes (opt-in) | History only | History only | History only | History only |
| Privacy Controls | Granular per-site | Standard | Standard | Strong | Strong |
| Built on Chromium | Yes | Yes (is Chromium) | Yes | No (Gecko engine) | Yes |
| Speed | Competitive | Fastest | Very fast | Good | Good |
| Market Position | New entrant | Market leader | Growing | Niche privacy | Privacy-focused |
| Price | Free (Plus/Pro for Agent Mode) | Free | Free | Free | Free |
Why Atlas Is Different:
Unlike Chrome, which relies on extensions for AI features and requires manual integration with external tools, Atlas bakes AI into the browser architecture itself. This means lower latency, better context retention, and a more cohesive experience.
Compared to Edge's Copilot integration, Atlas goes further with Agent Mode, allowing autonomous task completion rather than just summarization and chat.
Firefox and Brave prioritize privacy but have limited AI capabilities—they represent a trade-off between privacy and intelligence.
Google's upcoming Gemini 3.0 browser (expected before end of 2025) will be OpenAI's most direct competitor. Both will battle for the "AI-native browser" crown, but Atlas's head start, tight ChatGPT integration, and Agent Mode capabilities position it as the early leader.
The Technology Behind Atlas: Why This Matters
Atlas isn't just a clever frontend—it represents advances in several deep technical domains.
On-Device Processing and Latency Reduction
One of the biggest advantages Atlas has over web-based ChatGPT is latency. Opening ChatGPT in a separate tab, waiting for it to load, typing your query, and waiting for a response costs 10-15 seconds on average. With Atlas, the sidebar is always there, context is already loaded, and response time drops to sub-second for most queries.
On macOS, Atlas offers on-device summaries, meaning web content can be summarized locally without sending data to OpenAI's servers. This is a privacy win and a performance win.
Real-Time Web Access and Browsing Context
Atlas sees exactly what you see on the webpage in real-time. This allows ChatGPT to:
- Detect visual elements (images, tables, layouts) and reason about them
- Maintain continuous context as you navigate pages
- Offer suggestions based on the current page content
- Trigger actions only on pages you've explicitly visited
This is more sophisticated than traditional web search, which only has access to indexed text.
Fine-Tuned Models for Browsing Context
Atlas uses specialized models trained to understand browsing intent. OpenAI's engineering lead Ben Goodger stated that Atlas was built on the idea of "chatting with your browser"—meaning the underlying models were optimized for conversational browsing queries rather than general text generation. This matters because browsing queries are different from standalone ChatGPT queries. You're asking for contextual analysis, not just information retrieval.
Privacy and Data Control: OpenAI's Approach
OpenAI learned from criticism of its earlier products. Atlas includes privacy controls that many users have demanded.
What You Control:
- Visibility Toggle: A per-site toggle in the address bar lets you decide which websites ChatGPT can access. When visibility is off, ChatGPT can't see page content and no memories are created.
- Browser Memories: Entirely opt-in. Disabled by default. You can view, archive, and delete memories anytime.
- Incognito Mode: Temporarily logs you out of ChatGPT, so no chats or browsing history are saved to your account.
- Training Opt-Out: By default, browsing content is not used to train OpenAI's models. This is a significant privacy commitment.
- History Management: You can clear specific pages, your entire browsing history, or schedule automatic deletion.
Data Storage and Ownership:
Browser Memories are private to your ChatGPT account. No other workspace members can see them unless you share your account or device. Business and Enterprise users get additional admin controls over Browser Memory availability across their organization.
The architecture separates Browser Memories from ChatGPT Memories—they're controlled independently, giving you granular control over what's retained and how.
Emerging Threats and Security Measures:
OpenAI has addressed prompt injection vulnerabilities (sneaky website attempts to manipulate AI responses) with real-time detection and sandboxing. Agent Mode also includes protections: the agent operates only within browser tabs, cannot execute arbitrary code, and requires explicit approval for high-risk actions like financial transactions.
Real-World Use Cases: Where Atlas Creates Value
The theoretical benefits are clear, but where does Atlas solve real problems?
For Knowledge Workers and Researchers:
A researcher spending weeks on a competitive analysis can now ask Atlas to navigate competitor websites, collect pricing, feature comparisons, and customer reviews, then compile everything into a structured report. What used to take 20 hours now takes 2 hours.
A journalist researching a story can ask Atlas to synthesize information from multiple sources, pull relevant quotes, and fact-check claims across different websites without manually switching tabs.
For Sales and Business Development:
Sales professionals can use Agent Mode to research prospects, find recent company news, identify decision-makers, and draft personalized outreach emails—all within a single conversational flow. Lead qualification becomes faster and more data-driven.
For Students and Continuous Learners:
A student can read research papers, ask Atlas to explain complex concepts, have difficult passages rephrased, and compile study notes—all in one interface. Learning becomes more interactive and personalized.
For Customer Service and Support:
Support teams can use Atlas to research customer issues, find relevant documentation, draft responses, and escalate to human agents—reducing resolution time and improving consistency.
For E-Commerce and Shopping:
Shoppers can ask Atlas to compare products across multiple sites, read reviews, check prices, and make recommendations—transforming browsing into intelligent shopping assistance.
The Broader Implications: Why This Matters for the Future
Atlas represents a shift in how humans interact with technology. It's not just a browser—it's a template for what "AI-native applications" might look like.
For Google and Search:
Google's dominance in search is built on a simple model: type a query, get a list of links. Atlas threatens this model by offering direct answers with source verification, comparison, and synthesis. If Atlas captures significant market share, Google's advertising model—which depends on users clicking links—faces structural pressure.
OpenAI CEO Sam Altman stated the goal is to make browsers how people will use the internet in the future. This is an explicit challenge to Google's position.
For Enterprise Software:
If browsers become agents capable of taking actions across applications, the distinction between "browser" and "operating system" blurs. This could reshape how enterprise software is built, priced, and integrated.
For Privacy and Regulation:
Atlas's privacy controls will become a benchmark. If users experience granular control with Atlas and then compare it to Chrome's data collection practices, regulatory pressure on other browsers will intensify.
For the AI Industry:
Atlas validates a thesis the AI industry has been exploring: the best AI applications aren't ChatGPT clones or standalone tools, but AI deeply integrated into existing workflows. This will accelerate demand for embedded AI and vertical-specific agents.
Roadmap and Future Features
Atlas launched on macOS in October 2025. OpenAI has announced several upcoming capabilities:
- Windows Support: Expected in Q4 2025 or Q1 2026
- iOS and Android Apps: Mobile versions are planned but not yet released
- Voice-Based Browsing: Whisper AI integration could enable voice commands for browsing and Agent Mode tasks
- Third-Party Integrations: Plugins and extensions will allow deeper integration with productivity tools
- Enhanced Personalization: As Browser Memories mature, Atlas will offer increasingly personalized recommendations
Why the Gradual Rollout?
OpenAI is being cautious with Agent Mode and expansion. This reflects lessons learned from deploying powerful AI systems—safety, compliance, and user trust take precedence over speed. The company is testing edge cases, gathering user feedback, and refining the system before scaling.
How to Get Started with Atlas
Current Availability:
- macOS: Available now (October 2025)
- Windows: Coming soon
- iOS/Android: Coming later in 2025
Access Levels:
- Free Users: Full browser functionality, ChatGPT chat in sidebar, basic features
- ChatGPT Plus/Pro: Agent Mode (preview), advanced browsing features
- ChatGPT Business: Enterprise admin controls, additional privacy and compliance features
Initial Setup:
- Download Atlas from openai.com (macOS link provided during launch)
- Import bookmarks and settings from your current browser
- Sign in with your ChatGPT account
- Configure privacy settings in Settings > Data Controls
- (Optional) Enable Browser Memories if you want personalization
- (Pro users) Enable Agent Mode to start automating tasks
Privacy-First Setup:
- Disable Browser Memories by default and enable only for sites you trust
- Use the visibility toggle to hide sensitive sites (banking, health) from ChatGPT
- Use Incognito mode for truly private browsing
- Review stored memories weekly and delete irrelevant ones
The Competitive Landscape: Who Else Is Building AI Browsers?
OpenAI isn't alone. The race for the AI-native browser is heating up.
Google's Response: Google is developing a Gemini-powered browser experience and has AI Mode in Chrome. However, Google's internal conflicts (search vs. AI disrupting search) mean their browser strategy is less cohesive.
Perplexity's Comet Browser: Perplexity, an AI search company, is launching Comet, a browser designed around AI search and synthesis. Comet is a direct competitor to Atlas and positions itself as "search-first" rather than "chat-first."
Microsoft Edge with Copilot: Edge has integrated Copilot, but the integration is less tight than Atlas's ChatGPT integration. Copilot feels like an addon rather than a core architecture.
Brave and Privacy Browsers: Privacy-focused browsers haven't entered the AI browser race yet, but this represents an opportunity—a privacy-first AI browser could capture users concerned about both surveillance and AI.
Challenges and Limitations
Atlas isn't perfect, and there are legitimate concerns to address:
Agent Mode Safety: Even with safeguards, Agent Mode poses risks. Websites could deceive Atlas, or bad actors could craft malicious prompts. OpenAI is monitoring for abuse, but edge cases will emerge.
Data Security: Centralized Browser Memories create a valuable target for hackers. OpenAI must maintain fortress-level security to prevent breaches.
Regulatory Uncertainty: As browsers become agents capable of financial transactions, data collection, and decision-making, regulators will scrutinize them. FTC, EU regulators, and others may impose new requirements.
Vendor Lock-In: Tight integration with ChatGPT creates dependency on OpenAI's API. If OpenAI changes pricing or terms, users face switching costs.
Accessibility and Equity: Agent Mode sophistication may create a digital divide—users with sufficient context and language skills benefit most, while others lag.
The Strategic Significance: What Atlas Signals About the Future
Atlas is more than a browser. It's a thesis about the future of computing:
- AI is not an add-on; it's infrastructure. Future systems won't have "AI features"—they'll be AI-native from the ground up.
- Context is everything. The best AI experiences aren't standalone tools but systems deeply integrated into existing workflows.
- Productivity comes from automation of cognitive work. Atlas automates research, comparison, synthesis, and writing—core cognitive tasks that consume knowledge workers' time.
- The browser is the new operating system. As web applications dominate, whoever controls the browser controls the gateway to user intent and data.
- Privacy and power aren't contradictory. Atlas shows it's possible to build powerful AI features while offering granular user control over data.
Conclusion: The Paradigm Shift Is Here
OpenAI's Atlas represents a genuine paradigm shift, not incremental progress. It reimagines the browser from a passive retrieval tool into an intelligent, agentic partner. Chat, memory, and agency—three capabilities that together create a qualitatively different browsing experience.
Early adopters will see productivity gains. Researchers, knowledge workers, and anyone spending significant time on web-based tasks can now delegate parts of their work to Atlas.
But the broader significance is systemic. Atlas signals that the future of software is agent-driven, context-aware, and integrated. It raises the bar for what users expect from applications. And it challenges Google's dominance in the browser and search markets at a moment when AI is fundamentally reshaping how people find information.
Whether you adopt Atlas immediately or wait for the Windows and mobile versions, one thing is clear: this is how browsers will evolve. The question isn't whether AI browsers become mainstream, but how quickly competitors catch up to OpenAI's lead.
The browser wars just entered a new era.
Related Reading:
- The Rise of AI Agents in 2025: From Chat to Action
- AI Search vs Traditional SEO: How to Optimize Content for Gemini, ChatGPT, Perplexity in 2025
- AI Agents Are Replacing Chatbots in 2025: The Complete Enterprise Guide With Real Use Cases
- The Future of Work in 2025: How AI is Redefining Careers and Skills
- Agentic AI: Your New Virtual Coworker is Here
Tags
Share this post
Categories
Recent Posts
Opening the Black Box: AI's New Mandate in Science
AI as Lead Scientist: The Hunt for Breakthroughs in 2026
Measuring the AI Economy: Dashboards Replace Guesswork in 2026
Your New Teammate: How Agentic AI is Redefining Every Job in 2026
Related Posts
Continue reading more about AI and machine learning

AI as Lead Scientist: The Hunt for Breakthroughs in 2026
From designing new painkillers to predicting extreme weather, AI is no longer just a lab tool—it's becoming a lead researcher. We explore the projects most likely to deliver a major discovery this year.

Your New Teammate: How Agentic AI is Redefining Every Job in 2026
Imagine an AI that doesn't just answer questions but executes a 12-step project independently. Agentic AI is moving from dashboard insights to autonomous action—here’s how it will change your workflow and why every employee will soon have a dedicated AI teammate.

The "DeepSeek Moment" & The New Open-Source Reality
A seismic shift is underway. A Chinese AI lab's breakthrough in efficiency is quietly powering the next generation of apps. We explore the "DeepSeek Moment" and why the era of expensive, closed AI might be over.