Machine Learning for Beginners: A Step-by-Step Guide to Understanding ML in 2025
Machine learning can seem complex, but it doesn't have to be. This beginner's guide will walk you through the basics of ML in 2025, with clear examples.
TrendFlash
Introduction: The Brain-AI Interface
Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) are no longer science fiction. AI is making them practical. Soon, AI might be directly connected to your brain. This transforms everything—but with enormous risks.
What Is Neurotechnology?
Definition
Neurotechnology: Devices that interface brain with computers
Types
- Non-invasive: External sensors (EEG, fMRI)
- Invasive: Implanted in brain (Neuralink)
- Semi-invasive: Electrode grid on brain surface
What It Does
- Read brain signals (what are you thinking/feeling?)
- Send signals to brain (stimulate neurons)
- Connect brain to computer (direct interface)
- Augment cognition (enhance thinking)
Current State (2025)
Medical Applications (Approved)
- Paralysis: Brain-controlled prosthetics, wheelchairs
- Blindness: Brain-to-vision systems (early)
- Deafness: Brain-to-hearing systems
- Motor disorders: Stimulation therapy
Commercial Development
- Neuralink: Elon Musk's company, human trials starting
- Others: Multiple companies in development
- Goal: Consumer neurotechnology by 2030s
Research Stage
- Reading specific thoughts (not just brain activity)
- Direct brain-to-brain communication
- Memory enhancement/implantation
- Mood/emotion regulation
The Promise
Medical Benefits
- Cure paralysis (regain movement)
- Restore senses (blindness, deafness)
- Treat neurological disease (Parkinson's, Alzheimer's)
- Treat psychiatric conditions (depression, PTSD)
Cognitive Enhancement
- Direct access to information (no need to learn)
- Faster thinking (AI helping cognition)
- Perfect memory (record experiences)
- Enhanced creativity
The Vision
Brain + AI = superintelligence (human + computer hybrid)
The Risks
Risk 1: Hacking Your Brain
What if: Hackers access your brain-computer interface
Consequence: Control of your thoughts/actions
Worse: Forced memories, altered personality
Risk 2: Corporate Control
What if: Company controlling your brain interface owns your thoughts
Surveillance: Complete monitoring of your cognition
Manipulation: Subliminal advertising, propaganda directly to brain
Risk 3: Inequality
Rich have: Enhanced cognition (smarter)
Poor have: Nothing (fall further behind)
Result: Cognitive divide (some humans superhuman, others normal)
Risk 4: Addiction
Direct: Brain stimulation more addictive than drugs
Result: Widespread addiction to pleasure centers
Risk 5: Loss of Humanity
What if: Too much AI integration changes what it means to be human
Question: Where does human end, machine begin?
Risk 6: Medical Disasters
Malfunction: Brain implant fails, causes brain damage
Side effects: Personality changes, cognitive decline
Liability: What happens if it goes wrong?
The Ethical Questions
Question 1: Consent
Can you truly consent to brain alteration when you don't understand implications?
Question 2: Privacy
Who owns data from your brain? Your thoughts are most private thing.
Question 3: Autonomy
If AI in brain influences thoughts, are you still autonomous?
Question 4: Equity
If only rich get brain enhancements, does society split into subspecies?
Question 5: Identity
If your brain is half AI, who are you?
The Regulatory Gap
Current Regulation
Minimal (medical devices approved, but not consumer neurotechnology)
Needed Regulation
- Safety standards (brain implants safer than aspirin?)
- Privacy protections (brain data must be protected)
- Equity safeguards (not just for wealthy)
- Ethical review (independent oversight)
Status: Not in place (companies moving faster than regulation)
Timeline
2025-2027: Medical applications expand, human trials increase
2027-2030: Early consumer neurotech (limited, wealthy)
2030-2035: Broader adoption if safety proven
2035+: Mass neurotechnology (if it goes that direction)
Conclusion: The Brain Frontier
Brain-computer interfaces are coming. They could help disabled people (amazing). They could enhance human cognition (wonderful). Or they could become tools of control and inequality (nightmare). The outcomes depend on how we regulate and deploy them.
Explore more on emerging technologies at TrendFlash.
Share this post
Categories
Recent Posts
Opening the Black Box: AI's New Mandate in Science
AI as Lead Scientist: The Hunt for Breakthroughs in 2026
Measuring the AI Economy: Dashboards Replace Guesswork in 2026
Your New Teammate: How Agentic AI is Redefining Every Job in 2026
Related Posts
Continue reading more about AI and machine learning
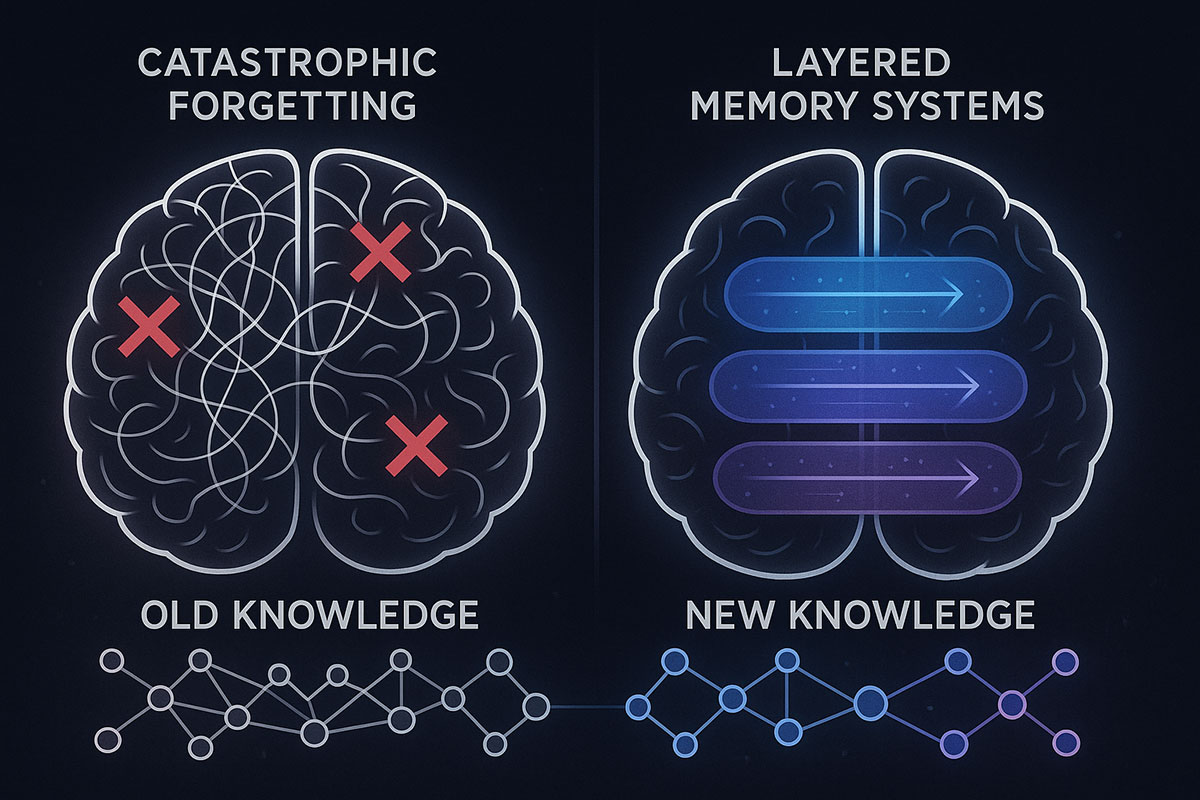
Google's HOPE Model: AI That Finally Learns Continuously (Catastrophic Forgetting Solved)
Google just unveiled HOPE, a self-modifying AI architecture that solves catastrophic forgetting—the fundamental problem preventing AI from learning continuously. For the first time, AI can absorb new knowledge without erasing what it already knows. Here's why this changes everything.
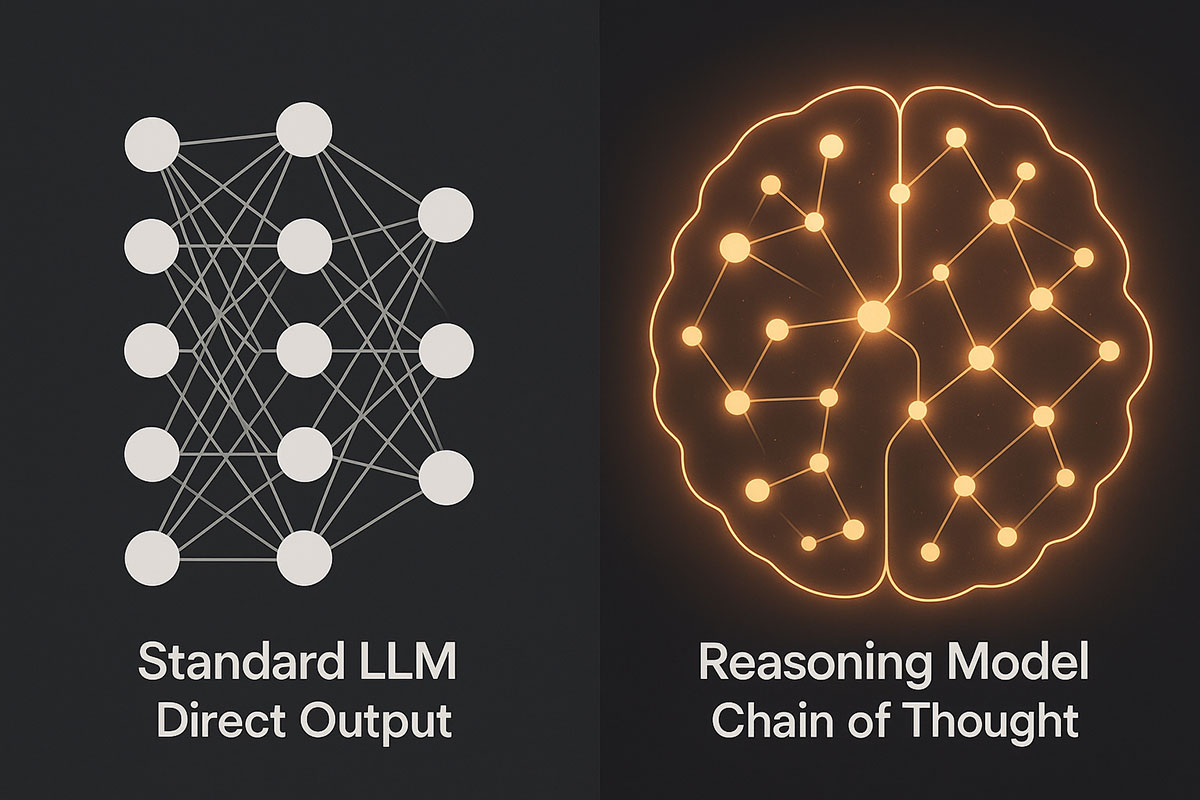
AI Reasoning Models Explained: OpenAI O1 vs DeepSeek V3.2 - The Next Leap Beyond Standard LLMs (November 2025)
Reasoning models represent a fundamental shift in AI architecture. Unlike standard language models that generate answers instantly, these systems deliberately "think" through problems step-by-step, achieving breakthrough performance in mathematics, coding, and scientific reasoning. Discover how O1 and DeepSeek V3.2 are redefining what AI can accomplish.
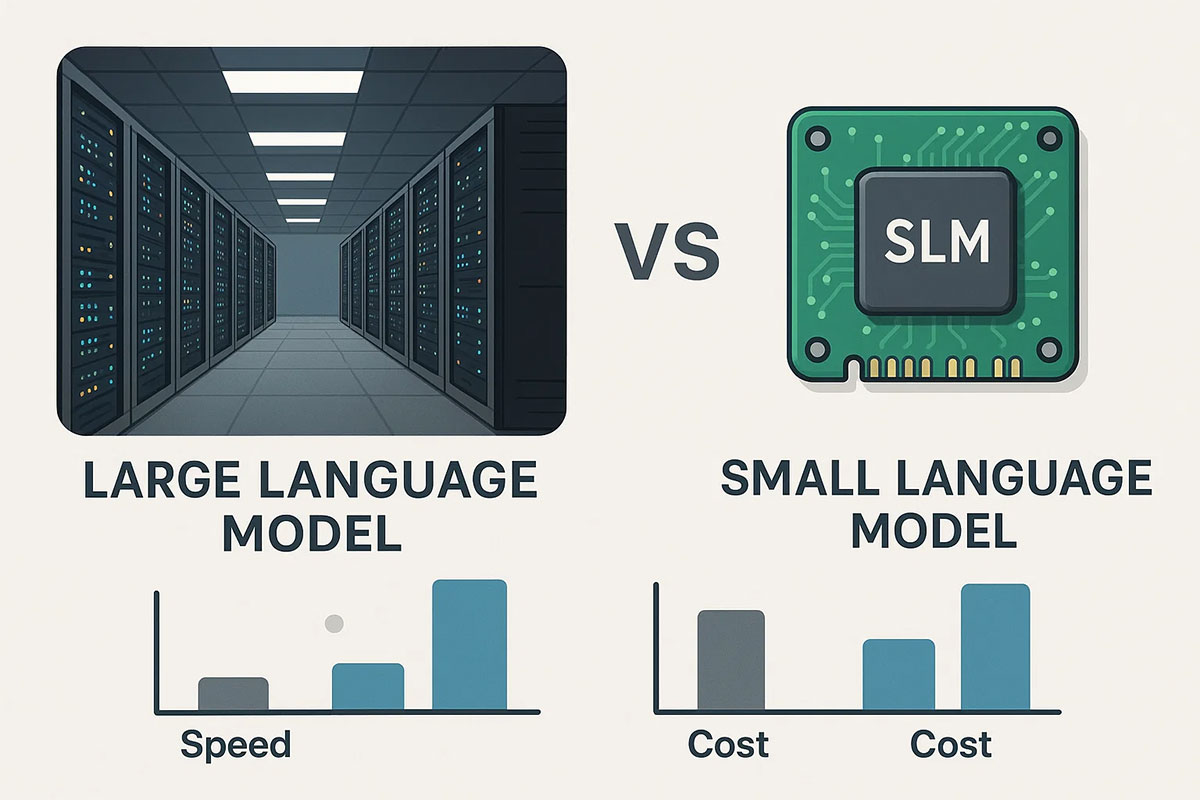
Why Smaller AI Models (SLMs) Will Dominate Over Large Language Models in 2025: The On-Device AI Revolution
The AI landscape is shifting from "bigger is better" to "right-sized is smarter." Small Language Models (SLMs) are delivering superior business outcomes compared to massive LLMs through dramatic cost reductions, faster inference, on-device privacy, and domain-specific accuracy. This 2025 guide explores why SLMs represent the future of enterprise AI.