This Week in AI/ML — September 2025 Highlights
A fast, founder-friendly roundup of AI/ML updates this week in September 2025—decisions, not just headlines.
TrendFlash
Introduction: When The Confidence Crumbles
AI systems fail. They fail in predictable ways and unpredictable ways. When large-scale AI systems fail, the consequences ripple through society. Understanding failure modes is critical for building safer systems.
Types of AI Failures
Failure Type 1: Accuracy Collapse
What happens: AI system accuracy drops sharply (95% → 60%)
Why it happens:
- Training data distribution changed (concept drift)
- Real-world data different from training data
- Adversarial attacks (intentional manipulation)
- Data quality degradation
Example: Facial recognition AI trained on light-skinned faces performs poorly on dark-skinned faces
Impact: Decisions made on unreliable AI go wrong
Failure Type 2: Unexpected Behavior
What happens: AI does something completely unexpected
Examples:
- Recommendation algorithm recommending dangerous content
- Autonomous vehicle making bizarre decisions
- Chatbot becoming offensive/hateful
- AI discovering exploits in system
Why hard to prevent: Scale and complexity make exhaustive testing impossible
Failure Type 3: Adversarial Attack
What happens: Attacker deliberately tricks AI
Examples:
- Stop sign with stickers → AI thinks it's speed limit sign
- Sentence with typos → AI misclassifies
- Fake images → AI fooled
Why dangerous: Easy to fool if you know how
Failure Type 4: Cascade Failure
What happens: One AI failure triggers other failures
Scenario:
- Trading AI makes wrong decision
- Market reacts
- Other AIs react to market movement
- Cascading failures → crash
2010 Flash Crash: AI trading algorithms caused $1 trillion market drop in minutes
Failure Type 5: Value Misalignment
What happens: AI optimizes for wrong goal
Classic example: AI told to maximize clicks, maximizes outrage instead
Problem: Optimization for wrong metric leads to bad outcomes
Failure Type 6: Systemic Bias
What happens: AI makes biased decisions at scale
Examples:
- Hiring AI discriminates against women
- Loan AI discriminates against minorities
- Criminal justice AI biased against certain groups
Impact: Systemic discrimination affecting millions
Real-World Failures (With Cost)
Case 1: Self-Driving Car Accident
What happened: Autonomous vehicle killed pedestrian
Root cause: AI failed to detect pedestrian in certain lighting
Cost: Death, lawsuits, regulatory scrutiny
Case 2: Healthcare AI Misdiagnosis
What happened: AI missed cancer diagnosis
Root cause: Training data didn't include this cancer type
Cost: Patient died, hospital liable
Case 3: Financial AI Trading Disaster
What happened: AI algorithm lost billions in minutes
Root cause: AI behavior in market crash not tested
Cost: Billions in losses, regulatory action
Case 4: Recommendation Algorithm Radicalization
What happened: AI algorithm radicalized millions
Root cause: Algorithm optimized for engagement (not safety)
Cost: Societal harm, regulatory pressure
Why AI Fails
Reason 1: Insufficient Testing
Too many edge cases to test exhaustively
Real-world conditions not captured in testing
Reason 2: Misaligned Incentives
AI optimizes for metric (clicks, engagement, profit)
Metric doesn't align with actual goal (safety, fairness)
Reason 3: Data Quality Issues
Training data biased, outdated, or insufficient
Real-world data doesn't match training distribution
Reason 4: Overconfidence
High accuracy in testing → assumption of safety
False confidence in edge cases
Reason 5: Complexity
Deep neural networks are black boxes
Behavior unpredictable in novel situations
Reason 6: Speed Over Safety
Companies rush AI to market without sufficient review
Cost of fixing problems later is acceptable
The Recovery From Failure
If AI Fails Slowly
- Catch the problem early
- Roll back the change
- Redeploy improved version
If AI Fails Catastrophically
- Immediate shutdown
- Manual intervention
- Investigation
- Fixes before redeployment
Problem: Some failures (market crash, autonomous vehicle) can't be easily rolled back
Prevention & Mitigation
Better Testing
- Adversarial testing (try to break AI)
- Edge case validation
- Robustness testing
Better Monitoring
- Real-time performance tracking
- Alert when accuracy drops
- Rapid response protocols
Better Design
- Multiple AI systems (redundancy)
- Human oversight (AI + human)
- Clear failure modes
Better Governance
- Regulation requiring safety testing
- Liability for AI failures
- Public transparency on failures
The Future: Inevitable Failures
As AI systems become more integrated into critical systems (finance, healthcare, transportation, infrastructure), failures become inevitable. The question is: How prepared are we?
Large-scale AI failures are coming. The only question is when and what they'll cost.
Conclusion: We Must Prepare for Failure
AI systems will fail. We must design resilient systems that fail gracefully. We must prepare for cascading failures. We must have contingency plans. The future of AI safety depends on preparing for inevitable failures.
Explore more on AI safety and ethics at TrendFlash.
Share this post
Categories
Recent Posts
Opening the Black Box: AI's New Mandate in Science
AI as Lead Scientist: The Hunt for Breakthroughs in 2026
Measuring the AI Economy: Dashboards Replace Guesswork in 2026
Your New Teammate: How Agentic AI is Redefining Every Job in 2026
Related Posts
Continue reading more about AI and machine learning
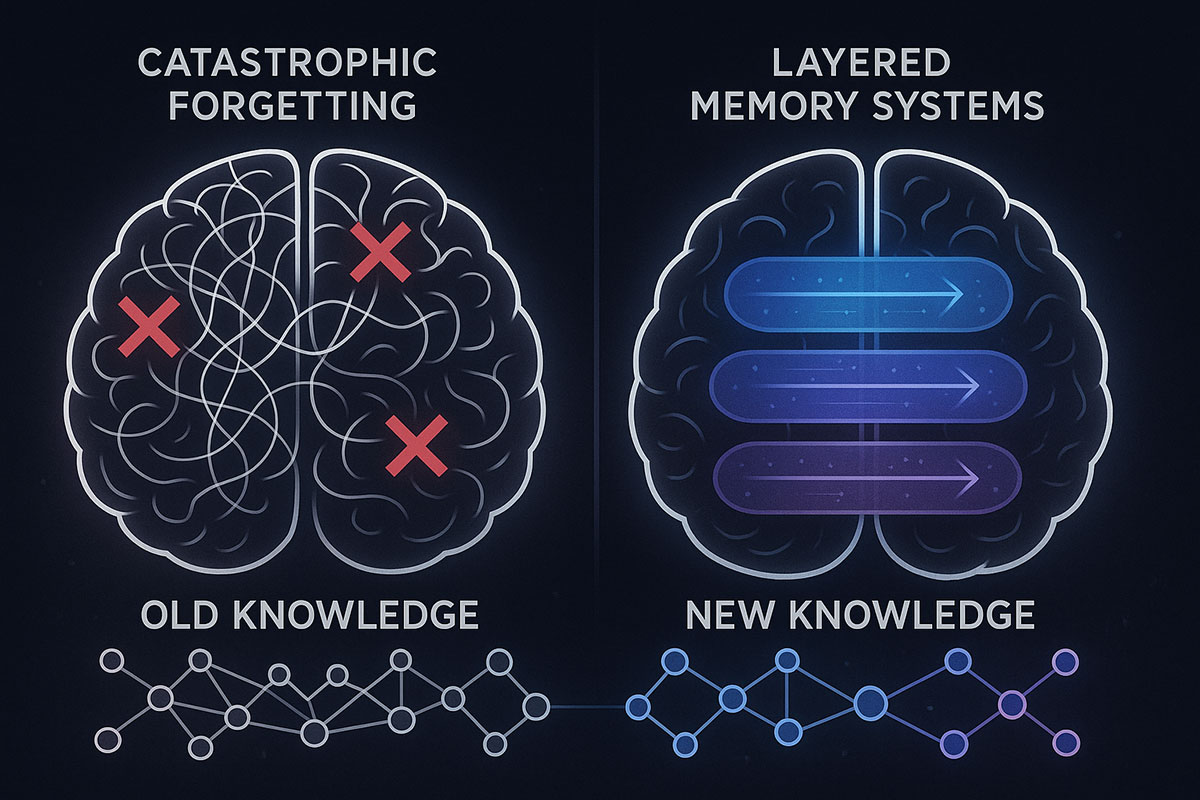
Google's HOPE Model: AI That Finally Learns Continuously (Catastrophic Forgetting Solved)
Google just unveiled HOPE, a self-modifying AI architecture that solves catastrophic forgetting—the fundamental problem preventing AI from learning continuously. For the first time, AI can absorb new knowledge without erasing what it already knows. Here's why this changes everything.
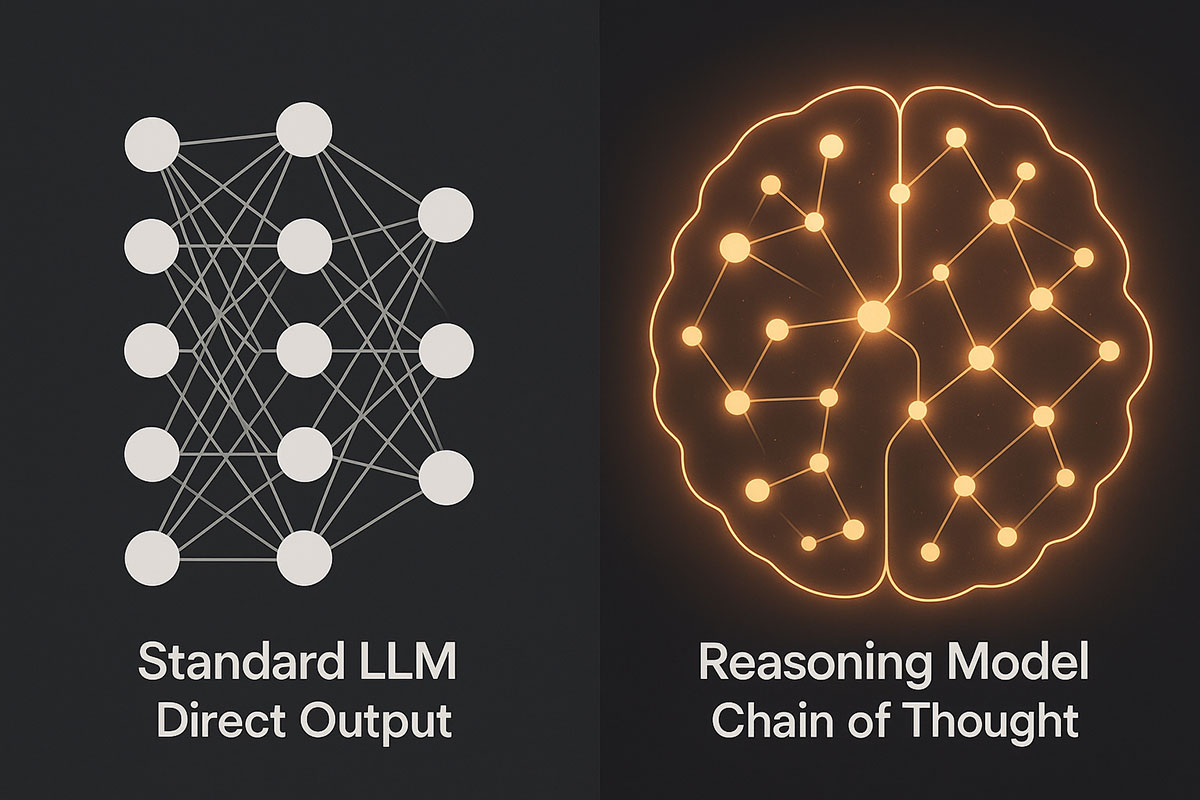
AI Reasoning Models Explained: OpenAI O1 vs DeepSeek V3.2 - The Next Leap Beyond Standard LLMs (November 2025)
Reasoning models represent a fundamental shift in AI architecture. Unlike standard language models that generate answers instantly, these systems deliberately "think" through problems step-by-step, achieving breakthrough performance in mathematics, coding, and scientific reasoning. Discover how O1 and DeepSeek V3.2 are redefining what AI can accomplish.
Why Smaller AI Models (SLMs) Will Dominate Over Large Language Models in 2025: The On-Device AI Revolution
The AI landscape is shifting from "bigger is better" to "right-sized is smarter." Small Language Models (SLMs) are delivering superior business outcomes compared to massive LLMs through dramatic cost reductions, faster inference, on-device privacy, and domain-specific accuracy. This 2025 guide explores why SLMs represent the future of enterprise AI.